Diatonic scales are widely used scales in music. However, there is some confusion about what is and what is not a diatonic scale. In this post we are going to clarify it.
What are diatonic scales?
To understand what a diatonic scale is we need to look at some characteristics that distinguish it from other scales:
- A diatonic scale is a scale of seven sounds.
- It goes by joint degrees (no jumps).
- Has the largest number of major and minor chords
- It has five tones and two semitones.
- If there are more than 4 consecutive tones it is not diatonic even if the above rules are met
For the scale to be considered diatonic, all the above points must be fulfilled. Let’s see some examples to understand it better:
Identifying diatonic scales
Does it have seven sounds?
There are several scales that have seven sounds. The most common are:
- Major scales. E.g. DO RE MI FA SOL LA SI
- The minor scales. E.g. LA SI DO RE MI FA SOL
- Harmonic scales. E.g. LA SI DO RE MI FA SOL#.
- Melodic scales. Ex. LA SI DO RE RE MI FA# SOL# SOL#
An example of scales that are not 7 sounds could be the scaleblues or A scale pentatonic therefore they are already excluded. On the other hand, it is also important to keep in mind that there are several scales that are not 7 sounds. scales major minor scales, harmonic y melodic.
Are there any separations or jumps of more than two or three notes?
The scales in point 1 have no leaps, so we still consider them diatonic. They have passed the test! (FOR MOMENT!)
Now let’s see which scales have leaps in order to distinguish them from diatonic scales:

As you can see, the A minor scale goes by joint degrees, that is to say, there are no jumps. On the other hand, the pentatonic minor scale does have them. Besides, it does not fulfill the requirement of point 1, which is to have 7 notes, since it has only five.
With this point it is clear that any scale that does not have jumps and has seven notes could be diatonic.
Does it have the largest number of major and minor chords?
First of all I recommend that you watch this video so that you can understand what I want to explain:
Flash explanation for beginners: Chords are formed by placing one note on top of another. If you have a line the next note will go on the line above and if you have space in the space.
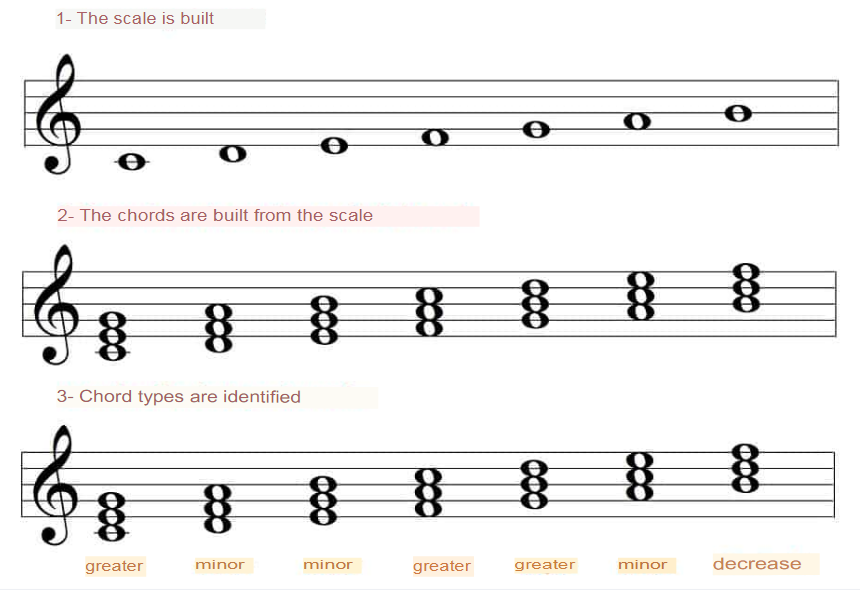
As you can see in the image, in a major scale we have three major chords, two minor chords and one diminished chord.
It has 5 tones and 2 semitones.
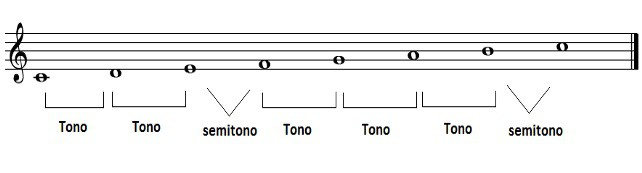
This filter is the most important! With the major scale, as with the natural minor scale and the modes, we have a structure of 5 tones and 2 semitones.
This refers to the distance between each of the notes that make up the scale. Let’s see the example of tones and semitones of the major scale:
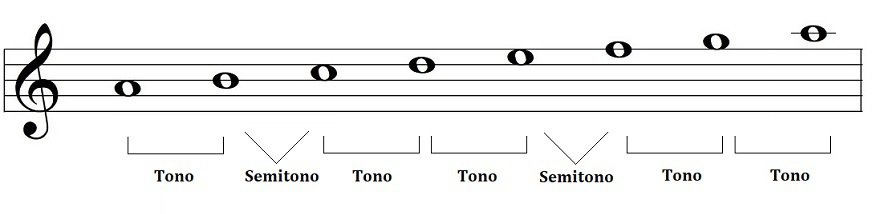
The same thing happens with the natural minor scale, but in a different order of tones and semitones:
However, the melodic minor scale and the harmonic minor scale, despite having 7 notes does not meet this requirement. Let’s see why:
The harmonic and melodic minor scale: Are they diatonic?
These scales have 7 sounds plus their octave, plus they go by joint degrees. But the following happens:
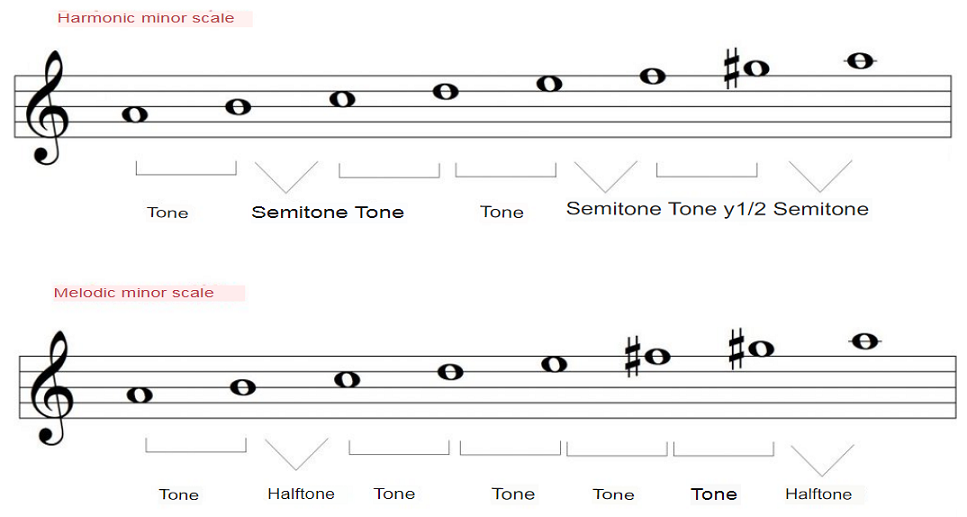
The harmonic minor scale has one and a half tones and 3 semitones. On the other hand, the melodic minor scale has 5 tones and 2 semitones but it has more than three tones in a row, so it is also discarded. That is, we only have the major scale and the natural minor scale as diatonic scales.
Knowing this, we would also say that the modes, as they are constructed, are also diatonic:
What are the modes in diatonic scales?
Diatonic scales have different modes. A mode is basically a major scale starting on a different note of the scale each time. That is, if the C scale has 7 notes. There are 7 different modes. One for each note. Watch this short explanation and you will understand:
If the modes are built from the major scale, they will logically have 5 tones and 2 semitones.
Common questions about diatonic scales:
Are all diatonic scales major?
As we have seen, not only major scales, but also natural minor and modal scales.
What is the diatonic scale used for?
The diatonic scale is useful to know the key we are in. For example if we want to compose a melody and have it make some sense, it is important to understand which notes within the scale and which diatonic chords we are going to use. Also if you are not going to use diatonic chords, know why they are not diatonic and how to sound good out of the diatonic sound.
How are diatonic scales formed?
The diatonic scales are the major, natural minor and modes.
What is the difference between the diatonic scale and the chromatic scale?
As we have seen above, diatonic scales have very specific characteristics. A short definition of the chromatic scale is that it is a scale that has only semitones.
I hope you liked this post and I hope you understood the concept of diatonic scale, don’t forget to share and spread the knowledge!